Trade Carbon Credits Do
A new market is emerging in the form of carbon credits, which are issued by companies as compensation for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The goal of this market is to decrease the cost of new technologies to reduce emissions. There are two types of markets: the regulatory market and the voluntary market. The latter allows individuals to purchase credits for themselves, while the former is limited to businesses.
The price of trade carbon credits depends on a number of factors, such as the supply and demand of the economy and the nature of the project. There are several different kinds of projects that are issued credits, including industrial and community-based initiatives.
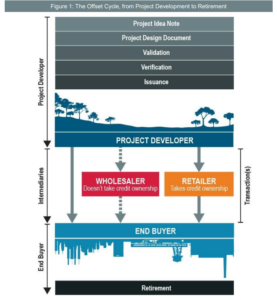
These projects are typically larger-scale and produce large volumes of credits. They can trade at a premium to industrial projects because of the added social and environmental benefits. There are also community-based projects that are more locally focused. They tend to have more specific rules and regulations, which can have a direct effect on the pricing of these credits.
What Does Trade Carbon Credits Do?
In the U.S., for instance, there are currently no national carbon markets, which means that American companies and individuals are reliant on the California Cap-And-Trade program. This program limits the amount of emission permits a business can buy or sell, and it is up to the company to find a way to offset its carbon emissions.
The United States is one of the leaders in the fight against climate change. This is in part due to the efforts of Senator John Kerry, who has proposed a framework linking carbon credits to fossil fuels. The plan is being promoted at the COP27 climate summit in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt. It would reward countries with credits for reducing power generation and replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy.
The US plan was reported in the Financial Times. In addition to limiting the number of permits available to participating businesses, the plan encourages investment in cleaner production alternatives. This is likely to lead to a tenfold increase in the price of carbon credits in the coming decade, according to recent studies.
However, even though the price of carbon credits is on the rise, the process of putting a price on these products isn’t exactly simple. There are a number of regulations that make putting a price on these credits possible, but they aren’t as rigorous as some might expect. In addition, there’s no way to verify if a company actually did its part to offset its emissions.
The most significant thing to note about these carbon credits is that they can be purchased or sold over international borders, making them an ideal investment for anyone looking to benefit from climate change. These assets can be bought from a number of different sources, including brokers and retailers. A number of carbon ETFs are available to investors, as well. The best place to begin is to research the specific carbon market in which you’re interested in investing.